Welcome to our insightful exploration of a remarkable investment journey! Today, we’re diving into the world of artificial intelligence (AI) and stock market phenomenons. Buckle up as we uncover the story of a stock that has skyrocketed by an astounding 230,000% since its IPO and still promises immense growth opportunities. Our journey will be filled with fascinating insights, playful anecdotes, and a touch of modesty, ensuring an engaging read from start to finish.
Unveiling the Phenomenal Growth of Amazon and Its AI Ventures
In the heart of the 22nd-century metropolis, the vibrant colors of Amazon’s logo are splashed across the sky, a beacon of the city’s tech-driven evolution. The logo is not merely an advertisement but a symbol of the city’s lifeblood, with Amazon’s ecosystem integrated into every aspect of urban life. The sky is abuzz with the hum of drones, their sleek frames bearing the familiar black and orange insignia. They weave through the air like a well-choreographed dance, delivering packages, monitoring traffic, and even assisting in emergency services. The streets below are a symphony of autonomous vehicles, their electric engines producing little more than a soft whirr as they navigate the cityscape with fluid efficiency. The buildings, too, are alive with technology, their smart facades adapting to the environment, absorbing sunlight during the day and illuminating the streets at night with a soft, energy-efficient glow.
Yet, this futuristic cityscape is not without its controversies. While some see Amazon’s omnipresence as a symbol of innovation and convenience, others view it as a stark reminder of corporate dominance and consumer surveillance. The AI-driven technologies, from the drones to the smart buildings, raise questions about privacy and data security. The autonomous vehicles, while efficient, have sparked debates about job displacement and the ethical dilemmas of AI decision-making. Despite these concerns, the city thrives, a testament to the relentless march of technology and the complex role of corporations in shaping the future of urban life.
The Rise of Generative AI
Generative AI, a subset of artificial intelligence, refers to algorithms designed to create new content, such as images, music, or text, that is similar to its training data. Unlike discriminative AI, which focuses on classification and prediction, generative AI learns patterns and generates new, synthetic yet realistic data. Its impact on various industries is profound and multifaceted.
In numerous sectors, companies are leveraging generative AI to create value and save time and money. Here’s how:
- In pharmaceuticals, it’s accelerating drug discovery by predicting how different compounds will behave, saving vast amounts of resources normally spent on physical testing.
- In entertainment, it’s used to create realistic characters, environments, and even generate scripts or music, reducing production times and costs.
- In manufacturing, it optimizes design and production processes by generating and evaluating countless prototypes.
- In customer service, it powers advanced chatbots that can understand and respond to customer inquiries more naturally and effectively.
However, it’s not without its challenges. Generative AI can sometimes produce inappropriate or low-quality content, and it can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in its training data. Moreover, there are concerns about job displacement and the ethical implications of AI-generated content.
The market for generative AI is expected to grow significantly, with some estimates projecting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 20.5% from 2021 to 2028. This growth is attracting so much attention for several reasons:
- Generative AI’s potential to disrupt and transform industries, creating new opportunities and business models.
- Its ability to democratize content creation, enabling anyone to generate art, music, or other creative works.
- The investment potential it presents, with venture capitalists and corporations increasingly backing generative AI startups.
- The technological advancements it brings, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible with AI.
Yet, the hype around generative AI should be tempered with caution. It’s essential to address its ethical implications, mitigate potential misuses, and ensure its benefits are distributed equitably.
Amazon’s AI Initiatives
Amazon’s foray into the AI realm is a strategic move that leverages its vast cloud infrastructure to offer a suite of AI solutions tailored to diverse client needs. Amazon Web Services (AWS) has adopted a three-tiered approach to cater to different levels of AI expertise and requirements. The first tier targets businesses seeking pre-built AI services, such as Amazon Rekognition for image and video analysis, Amazon Comprehend for natural language processing, and Amazon Forecast for time-series forecasting. These services allow companies to integrate AI capabilities without the need for extensive in-house expertise. The second tier is aimed at businesses with some AI experience, offering tools like Amazon SageMaker, which provides a fully managed service for building, training, and deploying machine learning models. The third tier caters to advanced users, providing the necessary infrastructure and tools to build AI solutions from scratch. This multi-tiered approach ensures that Amazon can serve a wide range of clients, from small startups to large enterprises, each with varying levels of AI proficiency.
A significant development in Amazon’s AI strategy is the introduction of Amazon Bedrock, a fully managed service designed to make foundation models—large AI models trained on vast amounts of data—more accessible and easier to use. Bedrock integrates seamlessly with AWS, allowing customers to build and scale generative AI applications using foundation models from leading AI companies, including Amazon. This service addresses several key challenges in AI deployment, such as the complexity of managing large models and the high computational resources required. By offering Bedrock, Amazon aims to democratize access to advanced AI capabilities, enabling businesses to innovate more rapidly. However, the success of Bedrock will depend on its ability to deliver on its promises of ease of use and scalability, as well as its competitive pricing and performance compared to other AI services.
In addition to its software offerings, Amazon is also investing in custom hardware development, particularly in the realm of Graphics Processing Units (GPUs). Amazon’s Trainium and Inferentia chips are designed to accelerate machine learning training and inference, respectively. This move positions Amazon as a direct competitor to Nvidia, which has long dominated the GPU market. While Amazon’s custom GPUs offer potential advantages in terms of cost and integration with AWS, they also face significant challenges. Nvidia’s GPUs are widely adopted and supported by a vast ecosystem of software and developer tools. Amazon will need to demonstrate that its GPUs can match or exceed Nvidia’s performance and compatibility to persuade businesses to switch. Moreover, the rapid pace of AI hardware innovation means that Amazon must continually invest in research and development to stay competitive. The success of Amazon’s AI hardware initiatives will hinge on their ability to provide compelling performance and value to customers, while also fostering a robust ecosystem of supporting tools and services.
- Positive: Potential for cost savings and seamless integration with AWS.
- Negative: Faces stiff competition from established players like Nvidia.
- Challenge: Need for continuous innovation and ecosystem development.
The Future of Amazon Stock
Amazon’s stock has shown remarkable resilience and growth since the start of 2023, with a significant turnaround attributable to its strategic entrance into the generative AI arena. After a lackluster 2022, where the stock experienced a 12-month decline of nearly 50%, Amazon shares have since rebounded, achieving a notable 18% gain in the first half of 2023. This recovery has been largely driven by the market’s positive response to Amazon’s foray into AI, particularly its investment in and integration of generative AI technologies into its cloud computing arm, Amazon Web Services (AWS).
The impact of AI on AWS’s financial performance has been nothing short of transformative. Generative AI models, such as those used in AWS’s AI services, offer high margins due to their scalability and relatively low incremental costs. Here’s how AI is driving high-margin growth for AWS:
- AI services can be scaled rapidly without proportional increases in costs, leading to higher profit margins.
- Generative AI models can create new revenue streams by offering customers innovative solutions, such as personalized recommendations, predictive analytics, and automated content generation.
- AI can also enhance operational efficiency, reducing costs associated with data management, processing, and analysis.
While AI’s impact on AWS is overwhelmingly positive, there are potential challenges to consider. These include:
- High upfront costs associated with research and development of AI technologies.
- Potential market saturation or competition from other tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and IBM.
- Regulatory hurdles and ethical considerations related to AI, such as data privacy and job displacement.
Looking ahead, future growth opportunities for Amazon’s AI business are vast and multifaceted. Potential avenues for expansion and investment include:
- Edge AI, which involves deploying AI algorithms on local devices to enable real-time data processing and analysis.
- AI-driven automation in sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and retail, improving efficiency and reducing human labor requirements.
- AI-as-a-Service, a business model that enables customers to access AI tools and services via a subscription-based platform.
FAQ
What is generative AI and why is it important?
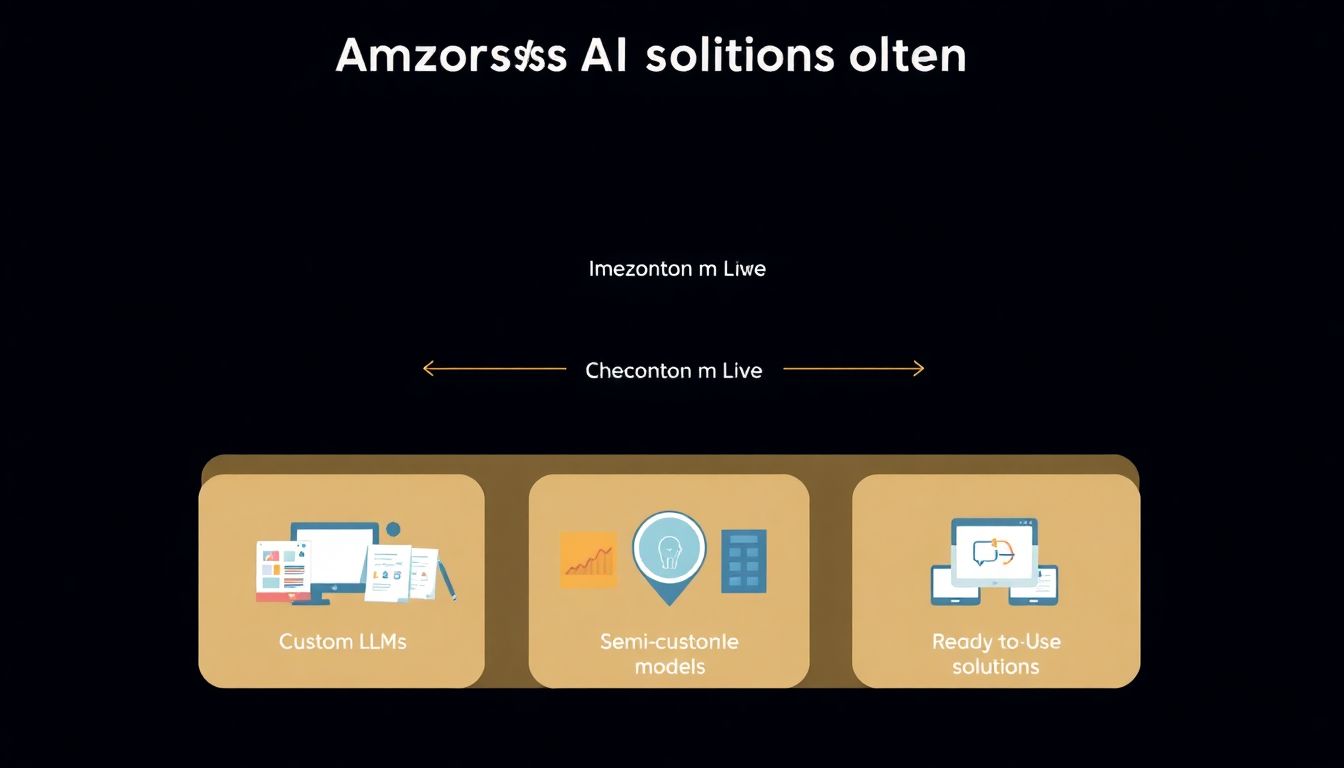
How is Amazon leveraging AI in its business?
- Developing custom large language models (LLMs) for clients
- Offering semi-customized generative AI models
- Providing ready-to-use AI solutions for smaller enterprises
- Building its own GPUs for generative AI
