Welcome to our in-depth exploration of how generative AI has transformed businesses two years after the launch of ChatGPT. We’ll delve into the real-world applications, challenges, and future prospects of this groundbreaking technology.
From Efficiency Gains to Cost Savings: A Deep Dive into Generative AI’s Impact on Businesses
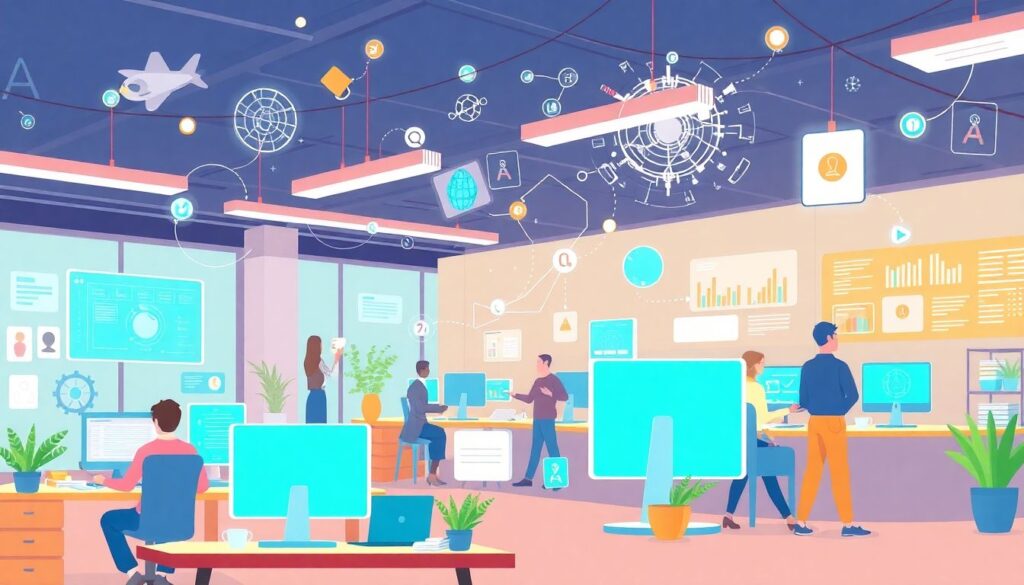
The illustration presents a panorama of a bustling office environment, where the hum of activity is not just from the chatter of employees but also from the silent, efficient whirring of AI-powered tools. These tools are not obtrusive gadgets but seamless extensions of the business processes, integrated with such finesse that they are barely noticeable. They are the smart coffee machine that remembers each employee’s preference, the AI-driven data analyzer that anticipates market trends, and the predictive system management tool that preempts tech glitches before they occur. The artwork subtly emphasizes the symbiotic relationship between human intelligence and artificial intelligence, where the latter augments the former, creating a synergistic ecosystem that thrives on productivity and innovation.
However, the illustration does not shy away from the potential challenges of such a workspace. While employees collaborate effortlessly, assisted by AI tools, there’s a subtle hint of dependency. The AI is ever-present, suggesting a degree of reliance that could potentially lead to complacency or a lack of human initiative. The artwork raises important questions about the balance between AI assistance and human autonomy, the need for continuous upskilling in an AI-driven workplace, and the potential privacy concerns in an environment where AI is always listening and learning. It provocatively asks the viewer to consider the fine line between AI integration and over-reliance, sparking a dialogue about the ethical and practical implications of AI in the modern office.
The Unsung Heroes: Everyday Applications of Generative AI
Generative AI has seamlessly integrated into our daily lives, subtly enhancing various industries, particularly customer service. Chatbots and virtual assistants, powered by generative AI, are often the first line of interaction for customers. These tools provide 24/7 support, drastically reducing response times and easing the workload on human agents. They can handle routine inquiries, manage simple tasks, and even provide personalized recommendations, leading to improved customer satisfaction. However, while these AI-driven systems offer consistency and scalability, they may lack the nuanced understanding and empathy of human agents, potentially leading to frustration in complex or sensitive situations.
In human resources, generative AI is quietly revolutionizing processes, from recruitment to employee engagement. AI can automate resume screening, ensuring candidates are evaluated purely on qualifications, thus reducing unconscious bias. It can also generate personalized onboarding materials and simulate training scenarios, helping new hires integrate more efficiently. Moreover, AI can analyze employee data to predict turnover rates and suggest proactive retention strategies. Nevertheless, over-reliance on AI in HR could lead to overlooked creative potential in candidates who do not fit conventional molds, or misjudgment of employee sentiment due to the subjective nature of human emotions.
The legal industry, known for its traditional methods, is also experiencing the touch of generative AI. It aids in document generation and automated contract review, saving countless hours of manual labor. AI can also predict legal outcomes based on similar cases, assisting lawyers in devising effective strategies. Furthermore, it can help make legal services more accessible through AI-powered chatbots that offer basic legal advice. However, the use of AI in law raises significant concerns, including data privacy and the potential for bias in algorithmic decisions, which could perpetuate existing inequalities in the legal system.
Challenges and Limitations: The Real-World Struggles
Generative AI, while promising, faces several challenges that hinder its widespread adoption. One of the most significant issues is reliability. Generative models can produce outputs that are not always accurate or relevant. This is often due to the nature of their training data or the stochastic processes involved. Experts like Gary Marcus, a professor emeritus of psychology and neural science at NYU, have repeatedly raised concerns about the reliability of generative AI, pointing out that these models often lack common sense and can generate plausible but false information. A study published in the Journal of Artificial Intelligence highlighted that generative models can be sensitive to input perturbations, leading to inconsistent outputs.
The cost-effectiveness of generative AI is another major challenge. Developing and deploying these models requires substantial computational resources and expertise. According to a McKinsey report, the total cost of ownership for generative AI can be prohibitive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises. Case studies, such as DeepMind’s AlphaFold project, illustrate that while the potential benefits are vast, the initial investment can be a significant barrier. Additionally, the ongoing costs of maintenance, updates, and data management can lead to long-term financial burdens.
Lastly, the readiness of companies to adopt generative AI is a critical limitation. Many organizations lack the necessary infrastructure, skills, and strategic vision to implement these technologies effectively. A survey by PwC found that while 72% of business executives believe AI will be a significant business advantage, only 33% are currently utilizing it. The hurdles include:
- Data governance and privacy concerns
- Integration challenges with existing systems
- A shortage of skilled AI talent
Furthermore, there is a cultural shift required to embrace the probabilistic nature of generative AI outputs, which can be at odds with traditional deterministic business processes.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Generative AI in Business
The future of generative AI in business is poised to revolutionize industries, with emerging trends and new use cases continually surfacing. At the current ‘crawl’ stage, businesses are exploring basic generative AI implementations, such as text generation for content creation and chatbots for customer service. These initial applications are already demonstrating significant value, automating routine tasks and enhancing customer interactions. However, they also present challenges, including the potential for generating inaccurate or biased content and the need for careful management of AI-generated outputs.
As businesses progress to the ‘walk’ stage, we expect to see more sophisticated use cases and an increase in revenue-generating applications. This may include:
- Personalized marketing campaigns, where generative AI creates tailored content for individual customers.
- Product design and development, with AI generating new ideas and prototypes based on vast datasets.
- Operational efficiency, using AI to predict and optimize complex systems and supply chains.
These advancements promise substantial financial benefits but also raise critical issues such as job displacement, data privacy, and the ethical use of AI.
In the long-term ‘run’ stage, generative AI has the potential to fundamentally transform industries. For instance:
- In healthcare, AI could generate personalized treatment plans and even new drugs tailored to individual patients.
- In entertainment, AI could create entirely new forms of media, from music to movies, tailored to specific audience preferences.
- In manufacturing, AI could design and produce entirely new materials and products.
However, realizing this future will require addressing significant challenges, including ensuring the transparency and explainability of AI decisions, mitigating the risks of misuse, and fostering a workforce equipped with the skills to work alongside AI systems. Companies that successfully navigate these challenges stand to gain a significant competitive advantage, while those that fall behind may find themselves increasingly marginalized.
FAQ
What are some common use cases for generative AI in businesses?
- Customer service chatbots to automate inquiries.
- Document summarization tools.
- HR automation for onboarding and vacation management.
- Legal document generation.
How do companies evaluate the ROI of generative AI investments?
- Assessing efficiency gains.
- Measuring cost savings.
- Analyzing the impact on productivity.
What are the main challenges companies face when implementing generative AI?
- Reliability issues.
- High cost of implementation.
- Lack of readiness in terms of technology and data.
How can businesses prepare for the future of generative AI?
- Starting with pilot projects.
- Focusing on internal efficiency first.
- Keeping an eye on emerging trends and technologies.
