Welcome to our insightful journey into the world of AI agents! As we step into the second quarter of the century, AI is no longer just a buzzword—it’s a transformative force reshaping industries. Today, we’re diving deep into the seven levels of AI agents, from basic reactive systems to the futuristic realm of superintelligent entities. Join us as we explore how these agents can revolutionize your business and prepare you for the AI-driven future!
A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses Navigating the AI Landscape
Imagine a sprawling, interconnected digital landscape, a futuristic hive of activity where various AI agents buzz with unparalleled efficiency. In the foreground, a customer service AI, embodied as a sleek, holographic figure, smoothly handles a myriad of customer queries, its circuits humming with empathy and problem-solving algorithms. Beside it, a marketing AI meticulously crafts personalized campaigns, its digital tendrils sifting through vast datasets to predict consumer behavior with uncanny accuracy.
Meanwhile, in the pulsating heart of the operations hub, a logistics AI orchestrates a symphony of delivery drones, their paths interweaving like a complex, aerial ballet. It communicates seamlessly with a procurement AI that scours the globe for the best deals, its digital eyes blinking with every transaction. Behind them, a towering AI-driven analytics engine looms, its surfaces shifting with ever-changing data visualizations, providing real-time insights to the AI agents and their human counterparts.
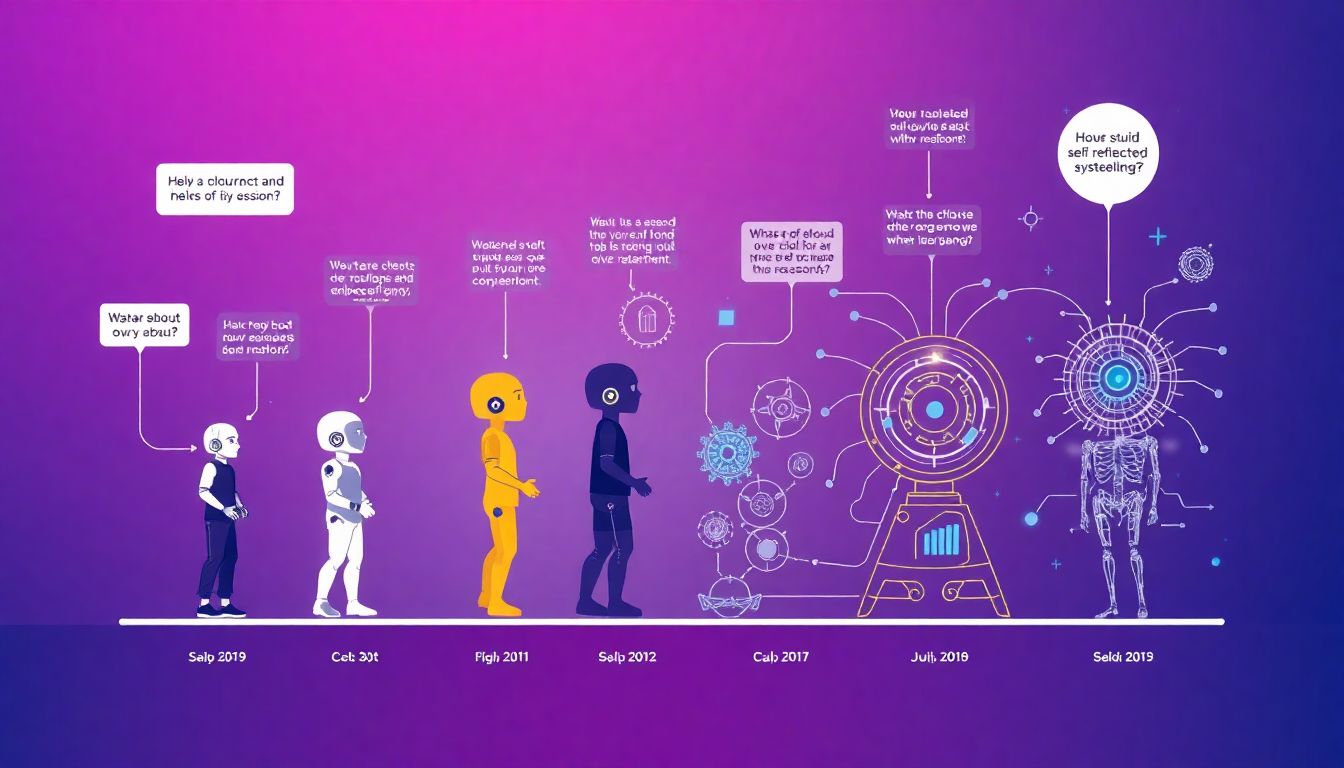
The Evolution of AI Agents
The evolution of AI agents, from simple reactive systems to hypothetical superintelligent entities, marks a trajectory of increasing complexity and capability. Early AI agents were simple reactive systems, like ELIZA, which operated on pre-programmed responses and lacked any true understanding or learning capabilities. These systems gradually evolved into ones that could learn from data, such as expert systems and early machine learning models. However, these models were still limited in their ability to generalize and adapt to new situations. As research progressed, AI agents evolved to include more advanced architectures, like deep learning models, that could learn hierarchical representations of data and generalize to a wider range of tasks.
As we move towards the future, the concept of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and superintelligence emerges. AGI refers to AI that understands, learns, and applies knowledge across various tasks at a level equal to or beyond human capabilities. Superintelligence, a step further, is an AI agent that possesses intelligence far surpassing that of the brightest and most gifted human minds in practically every economically valuable work. While these are still hypothetical, understanding this evolution provides a roadmap for organizations aiming to harness AI strategically.
Understanding the evolution of AI agents offers several benefits for organizations:
- It helps in identifying the current stage of AI development and what is coming next, allowing for better strategic planning.
- It provides insights into the increasing data requirements and computational resources needed for more advanced AI systems.
However, it also presents challenges:
- The need for continuous upskilling and reskilling of the workforce to keep up with AI advancements.
- The ethical implications and potential risks associated with more intelligent and autonomous AI systems.
By closely studying this evolution, organizations can anticipate and prepare for the opportunities and challenges that lie ahead, ensuring a more strategic and responsible integration of AI.
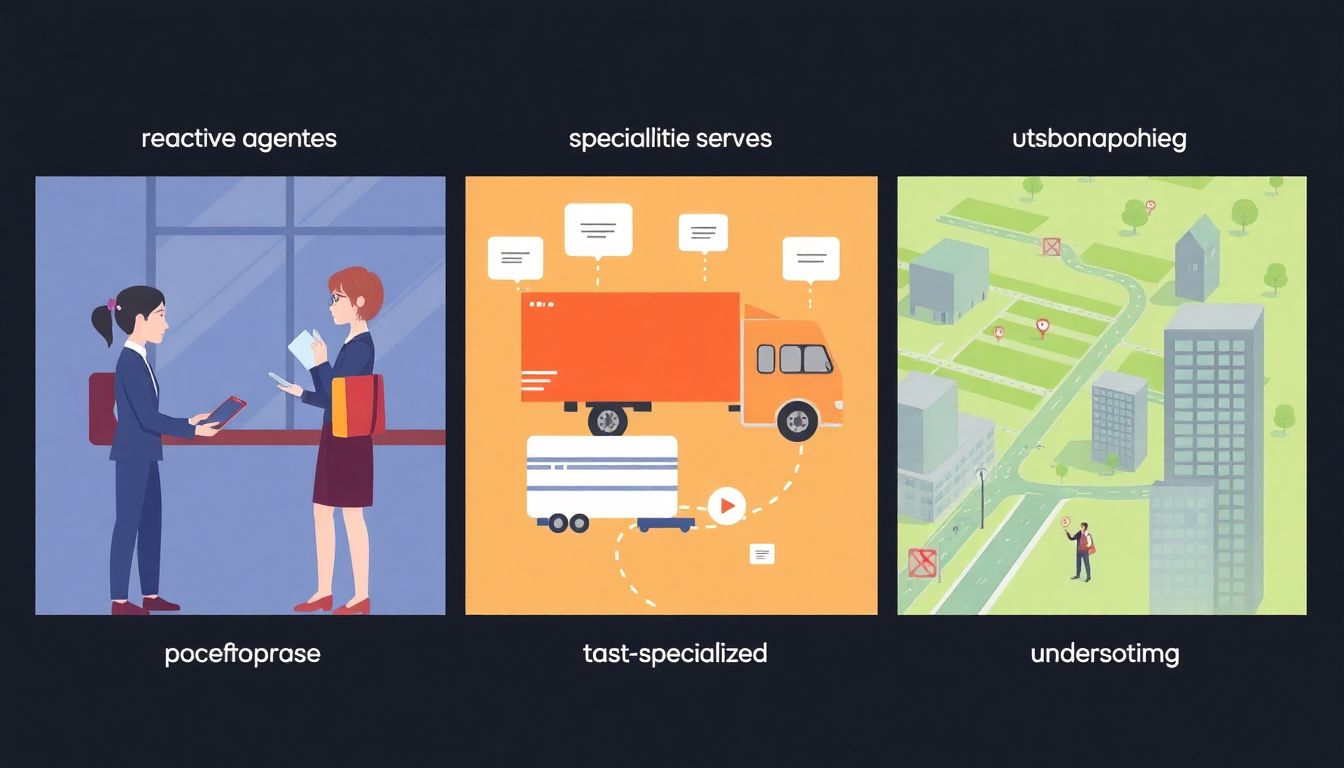
Levels 1-3: Foundational AI Agents
AI agents have evolved significantly over the years, with the first three levels—reactive agents, task-specialized agents, and context-aware agents—laying the foundation for AI’s role in various business applications.
Reactive agents are the simplest form of AI, designed to respond to immediate inputs without considering past experiences or future outcomes. These agents operate on a straightforward condition-action rule, making them highly efficient for automating repetitive tasks. In business, reactive agents are often employed in customer service chatbots that handle basic queries, such as FAQs or order tracking. For instance, a chatbot on an e-commerce site can quickly provide information about product availability or shipping details. While reactive agents excel in speed and consistency, they lack the ability to learn from interactions or adapt to new situations.
Task-specialized agents, on the other hand, are designed to perform specific tasks with a high degree of accuracy. These agents are trained on large datasets to specialize in particular domains, making them more versatile than reactive agents. Examples include:
- Fraud detection systems that analyze transaction data to identify suspicious activities.
- Recommendation engines that suggest products or services based on user preferences and behavior.
In business, task-specialized agents can significantly enhance operational efficiency. However, their reliance on predefined tasks means they may struggle with complex, dynamic scenarios that require a broader understanding of context.
Context-aware agents represent the next level of AI sophistication. These agents consider both the current situation and historical data to make informed decisions. By understanding the context, these agents can adapt to changing circumstances and provide more nuanced responses. Applications of context-aware agents in business include:
- Personal assistants that manage schedules, send reminders, and provide relevant information based on user behavior and preferences.
- Customer service systems that can handle complex queries, understand user sentiment, and provide personalized support.
While context-aware agents offer significant advantages, they also come with challenges. These agents require extensive training data and computational resources to function effectively. Additionally, ensuring the privacy and security of user data is a critical concern, as these agents often need access to sensitive information to operate effectively.
Levels 4-7: Advanced AI Agents
Advanced levels of AI agents, namely socially savvy agents, self-reflective agents, generalized intelligence agents, and superintelligent agents, present unprecedented opportunities and challenges for businesses. Socially savvy agents, equipped with advanced natural language processing and emotion recognition capabilities, can revolutionize customer service and human-AI interaction. They can understand and respond to human emotions, leading to more personalized and effective customer experiences. Self-reflective agents, capable of introspection and self-adjustment, can enhance decision-making processes by continuously learning from and improving their own performance. Generalized intelligence agents, which can understand and apply knowledge across various domains, can drive innovation and problem-solving in complex business environments.
However, the development of these advanced AI agents also raises significant challenges and ethical considerations. Here are some of the key points to consider:
-
Job displacement:
As AI agents become more capable, there is a risk of significant job displacement in sectors where human skills are mimicked or surpassed by AI.
-
Bias and fairness:
AI agents can inadvertently perpetuate or amplify existing biases if not designed with fairness in mind.
-
Transparency and accountability:
As AI agents become more autonomous, ensuring transparency in their decision-making processes and holding them accountable for their actions becomes increasingly complex.
-
Privacy concerns:
AI agents that handle sensitive data must be designed with robust privacy protections to prevent misuse or unauthorized access.
The development of superintelligent agents, which possess intelligence far surpassing human capabilities, presents even more profound transformative effects and ethical challenges. On one hand, superintelligent agents could drive unprecedented innovation and solve complex global challenges. On the other hand, they pose significant risks, such as existential risk, if not properly controlled or aligned with human values. To navigate these challenges, it is crucial to invest in AI governance, ethics research, and policy development. Businesses must also prioritize responsible AI development, emphasizing fairness, transparency, and accountability in their AI strategies.
FAQ
What are reactive agents and how can they benefit businesses?
- Example: A basic chatbot that answers questions based on keyword matching.
- Benefit: Efficient handling of customer inquiries, reducing response time and improving customer satisfaction.
How do task-specialized agents differ from reactive agents?
- Example: An e-commerce recommendation engine that suggests products based on user behavior.
- Difference: Unlike reactive agents, task-specialized agents can learn from data and improve their performance over time.
What are the key features of context-aware agents?
- Key Feature: Ability to synthesize diverse data sources to make informed decisions.
- Example: A financial fraud detection system that evaluates transaction patterns and user behaviors.
What are the challenges in developing self-reflective agents?
- Challenge: Ensuring the agent’s self-improvement does not lead to degraded performance.
- Solution: Developing robust feedback mechanisms and fostering a culture of iterative learning.
